A high percentage of individuals are frightened of seeing the dentist and find it nauseating to consider having dental work done. Fortunately, sedation dentistry in NYC allows dentists to offer their patients quality treatment while feeling relaxed and at ease in the dental chair.
 Sedation Types and Their Effects
Inhaled Minimal Sedation
For this type of sedation, nitrous oxide (often known as “laughing gas“) is inhaled through a mask. While the dentist performs the operation, nitrous oxide helps the patient calm down. The advantage of nitrous oxide is that it wears off relatively fast, allowing patients to leave the dental office unassisted and on their own.
Oral Sedation
The simplest form of sedation is oral. Your dentist will suggest that you take an oral sedative so you can relax. All you have to do is take a tablet about an hour before your appointment, and you’ll feel calm when you get there.
Depending on the amount, oral sedation can either make you sleepy or make you drowsy. It results in drowsiness that lasts longer and is stronger than nitrous oxide.
Halcion is a regular oral sedative (triazolam), and this can be straightforward to use. Aside from the fact that it’s taken orally, this type of sedation involves no needles. Many people who fear going to the dentist also fear using needles, which are necessary to deliver IV sedation. Instead of worrying about being poked by the dentist, the patient can take the sedative orally before the appointment.
IV Moderate Sedation
IV moderate sedation is administered intravenously (IV) into the patient’s veins. The drug can start working more quickly with this administration strategy. Because dentists can control the dose of sedation throughout the process, it’s a good sedative for lengthy procedures.
Long-lasting drowsiness, dizziness, headaches, visual abnormalities, forgetfulness, and nausea may be side effects of anesthetic or sedative medicines. Although uncommon, nausea and vomiting are possible adverse effects. For relief, bed rest and prescribed medications may be necessary.
General Anesthesia
Patients who receive deep sedation or general anesthesia are practically asleep the entire time. Deep sedation results in unconsciousness, in contrast to oral sedation or mild IV sedation, which induces patients to be drowsy but keeps them awake.
Deep sedation has the longest-lasting effects, and patients must wait for the effects to wear off before they can go home.
Which Is the Best for You?
The right sedative for you will depend on a few things, such as:
Sedation Types and Their Effects
Inhaled Minimal Sedation
For this type of sedation, nitrous oxide (often known as “laughing gas“) is inhaled through a mask. While the dentist performs the operation, nitrous oxide helps the patient calm down. The advantage of nitrous oxide is that it wears off relatively fast, allowing patients to leave the dental office unassisted and on their own.
Oral Sedation
The simplest form of sedation is oral. Your dentist will suggest that you take an oral sedative so you can relax. All you have to do is take a tablet about an hour before your appointment, and you’ll feel calm when you get there.
Depending on the amount, oral sedation can either make you sleepy or make you drowsy. It results in drowsiness that lasts longer and is stronger than nitrous oxide.
Halcion is a regular oral sedative (triazolam), and this can be straightforward to use. Aside from the fact that it’s taken orally, this type of sedation involves no needles. Many people who fear going to the dentist also fear using needles, which are necessary to deliver IV sedation. Instead of worrying about being poked by the dentist, the patient can take the sedative orally before the appointment.
IV Moderate Sedation
IV moderate sedation is administered intravenously (IV) into the patient’s veins. The drug can start working more quickly with this administration strategy. Because dentists can control the dose of sedation throughout the process, it’s a good sedative for lengthy procedures.
Long-lasting drowsiness, dizziness, headaches, visual abnormalities, forgetfulness, and nausea may be side effects of anesthetic or sedative medicines. Although uncommon, nausea and vomiting are possible adverse effects. For relief, bed rest and prescribed medications may be necessary.
General Anesthesia
Patients who receive deep sedation or general anesthesia are practically asleep the entire time. Deep sedation results in unconsciousness, in contrast to oral sedation or mild IV sedation, which induces patients to be drowsy but keeps them awake.
Deep sedation has the longest-lasting effects, and patients must wait for the effects to wear off before they can go home.
Which Is the Best for You?
The right sedative for you will depend on a few things, such as:
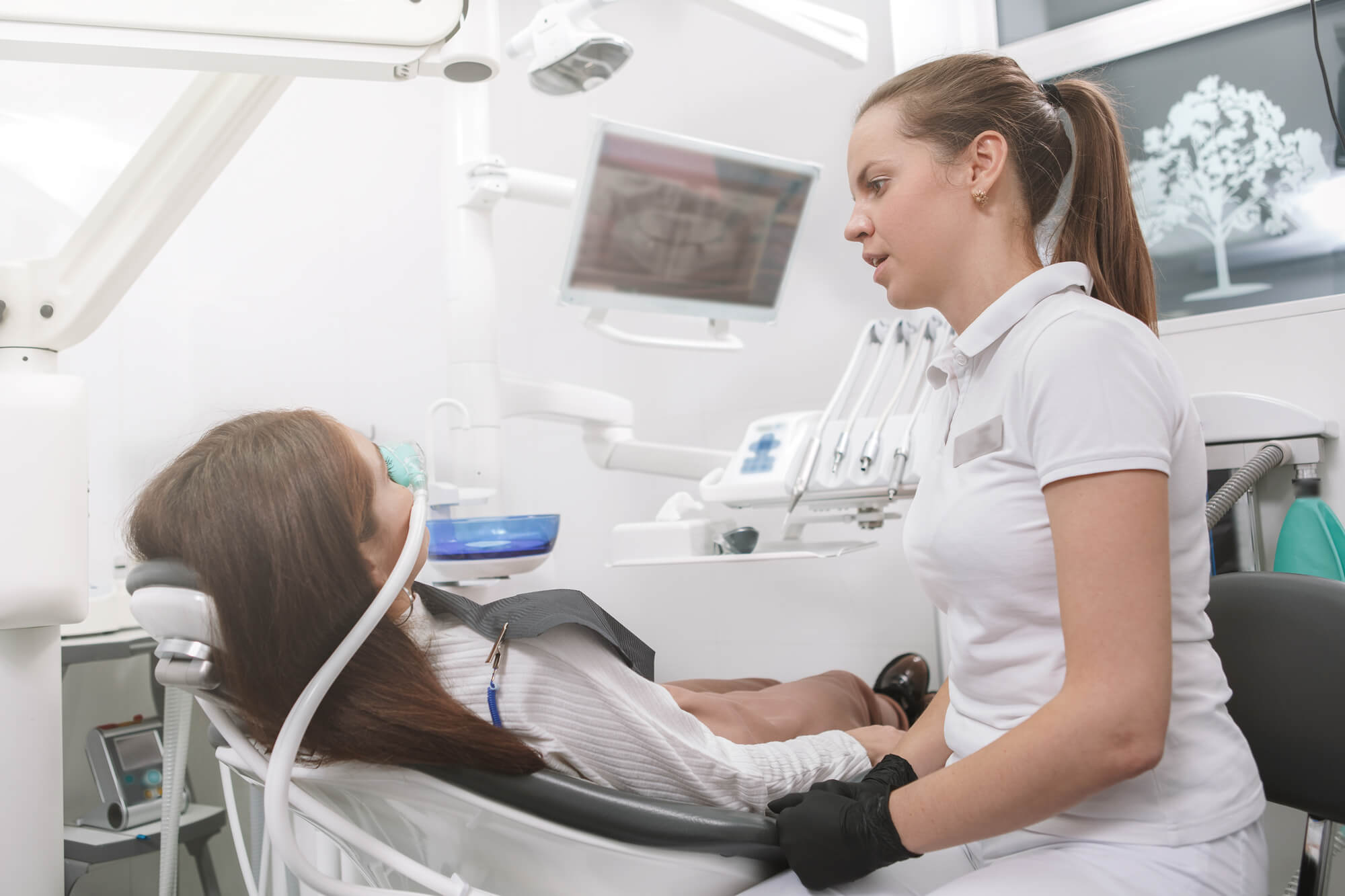 Learn More About Sedation Dentistry in NYC
If you want dental treatment completed by a professional who is not only highly skilled but also concerned with your comfort while you’re there, choosing Coliseum Dental is your best bet.
Learn More About Sedation Dentistry in NYC
If you want dental treatment completed by a professional who is not only highly skilled but also concerned with your comfort while you’re there, choosing Coliseum Dental is your best bet.
 Sedation Types and Their Effects
Inhaled Minimal Sedation
For this type of sedation, nitrous oxide (often known as “laughing gas“) is inhaled through a mask. While the dentist performs the operation, nitrous oxide helps the patient calm down. The advantage of nitrous oxide is that it wears off relatively fast, allowing patients to leave the dental office unassisted and on their own.
Oral Sedation
The simplest form of sedation is oral. Your dentist will suggest that you take an oral sedative so you can relax. All you have to do is take a tablet about an hour before your appointment, and you’ll feel calm when you get there.
Depending on the amount, oral sedation can either make you sleepy or make you drowsy. It results in drowsiness that lasts longer and is stronger than nitrous oxide.
Halcion is a regular oral sedative (triazolam), and this can be straightforward to use. Aside from the fact that it’s taken orally, this type of sedation involves no needles. Many people who fear going to the dentist also fear using needles, which are necessary to deliver IV sedation. Instead of worrying about being poked by the dentist, the patient can take the sedative orally before the appointment.
IV Moderate Sedation
IV moderate sedation is administered intravenously (IV) into the patient’s veins. The drug can start working more quickly with this administration strategy. Because dentists can control the dose of sedation throughout the process, it’s a good sedative for lengthy procedures.
Long-lasting drowsiness, dizziness, headaches, visual abnormalities, forgetfulness, and nausea may be side effects of anesthetic or sedative medicines. Although uncommon, nausea and vomiting are possible adverse effects. For relief, bed rest and prescribed medications may be necessary.
General Anesthesia
Patients who receive deep sedation or general anesthesia are practically asleep the entire time. Deep sedation results in unconsciousness, in contrast to oral sedation or mild IV sedation, which induces patients to be drowsy but keeps them awake.
Deep sedation has the longest-lasting effects, and patients must wait for the effects to wear off before they can go home.
Which Is the Best for You?
The right sedative for you will depend on a few things, such as:
Sedation Types and Their Effects
Inhaled Minimal Sedation
For this type of sedation, nitrous oxide (often known as “laughing gas“) is inhaled through a mask. While the dentist performs the operation, nitrous oxide helps the patient calm down. The advantage of nitrous oxide is that it wears off relatively fast, allowing patients to leave the dental office unassisted and on their own.
Oral Sedation
The simplest form of sedation is oral. Your dentist will suggest that you take an oral sedative so you can relax. All you have to do is take a tablet about an hour before your appointment, and you’ll feel calm when you get there.
Depending on the amount, oral sedation can either make you sleepy or make you drowsy. It results in drowsiness that lasts longer and is stronger than nitrous oxide.
Halcion is a regular oral sedative (triazolam), and this can be straightforward to use. Aside from the fact that it’s taken orally, this type of sedation involves no needles. Many people who fear going to the dentist also fear using needles, which are necessary to deliver IV sedation. Instead of worrying about being poked by the dentist, the patient can take the sedative orally before the appointment.
IV Moderate Sedation
IV moderate sedation is administered intravenously (IV) into the patient’s veins. The drug can start working more quickly with this administration strategy. Because dentists can control the dose of sedation throughout the process, it’s a good sedative for lengthy procedures.
Long-lasting drowsiness, dizziness, headaches, visual abnormalities, forgetfulness, and nausea may be side effects of anesthetic or sedative medicines. Although uncommon, nausea and vomiting are possible adverse effects. For relief, bed rest and prescribed medications may be necessary.
General Anesthesia
Patients who receive deep sedation or general anesthesia are practically asleep the entire time. Deep sedation results in unconsciousness, in contrast to oral sedation or mild IV sedation, which induces patients to be drowsy but keeps them awake.
Deep sedation has the longest-lasting effects, and patients must wait for the effects to wear off before they can go home.
Which Is the Best for You?
The right sedative for you will depend on a few things, such as:
- Type of Treatment
- Level of Comfort
 Learn More About Sedation Dentistry in NYC
If you want dental treatment completed by a professional who is not only highly skilled but also concerned with your comfort while you’re there, choosing Coliseum Dental is your best bet.
Learn More About Sedation Dentistry in NYC
If you want dental treatment completed by a professional who is not only highly skilled but also concerned with your comfort while you’re there, choosing Coliseum Dental is your best bet. 
